Java和C#对比(5):Java有但C#没有的地方和总结
1.受检查的异常
在异常这个概念出现之前,大多数异常处理都是通过返回代码进行。异常对于返回值来说有很多优势:
- 1.提供了一致的模型来处理错误和其它非预期的情况
- 2.如果没有在当前上下文中处理异常的话可以向上传播
- 3.开发者可以把处理错误的代码和普通业务逻辑分离 Java创建了额外的机制来处理受检查的异常和不受检查的异常。对于受检查的异常,调用的方法必须捕获异常,或通过throws声明异常必须被其调用方法处理。从另外一方面来说,不受检查的异常不需要catch也或用throws子句声明,不受检查的异常和返回代码一样不会让编译器出警告或错误,但是如果在运行时忽略异常的话同样会终止程序。受检查的异常一般用于告诉调用者如何和为什么会发生调用失败。不受检查的异常是一般程序中大部分地方都会发生的异常,如果都要进行显式检查的话开销比价值大。比如空对象引用的异常或是数组越界的异常,如果是收检查的异常话,就需要在每一个访问对象或访问数组的时候都进行try catch,因此比较适合不受检查的异常。
在C#中所有异常都是未收检查的异常,也没有throws子句。这么做的主要劣势是API只能通过文档来告诉调用者自己会抛出哪些异常。比如对于如下的代码,唯一知道下面方法会出现哪些异常的方法是查看所有调用方法的源代码或这些方法的源代码。
public string GetMessageFromServer(string server)
{
//Set up variables and String to write to the server
Encoding ASCII = Encoding.ASCII;
string Get = "GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: " + server +
"\r\nConnection: Close\r\n\r\n";
Byte[] ByteGet = ASCII.GetBytes(Get);
Byte[] RecvBytes = new Byte[256];
String strRetPage = null;
// IPAddress and IPEndPoint represent the endpoint that will
// receive the request
// Get first IPAddress in list return by DNS
IPAddress hostadd = Dns.Resolve(server).AddressList[0];
IPEndPoint EPhost = new IPEndPoint(hostadd, 80);
//Create the Socket for sending data over TCP
Socket s = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream,
ProtocolType.Tcp );
// Connect to host using IPEndPoint
s.Connect(EPhost);
if (!s.Connected)
{
strRetPage = "Unable to connect to host";
return strRetPage;
}
// Sent the GET text to the host
s.Send(ByteGet, ByteGet.Length, 0);
// Receive the page, loop until all bytes are received
Int32 bytes = s.Receive(RecvBytes, RecvBytes.Length, 0);
strRetPage = "Default HTML page on " + server + ":\r\n";
strRetPage = strRetPage + ASCII.GetString(RecvBytes, 0, bytes);
while (bytes > 0)
{
bytes = s.Receive(RecvBytes, RecvBytes.Length, 0);
strRetPage = strRetPage + ASCII.GetString(RecvBytes, 0, bytes);
}
return strRetPage;
}
上面的代码取自.NET框架Beta2文档的Socket类。注意到,在这段代码中没有捕获异常。如下是根据文档得出的这个方法可能抛出的异常:
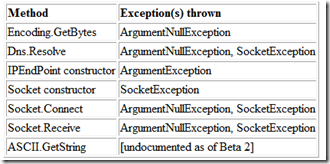
2.扩展
Java扩展机制允许开发者扩展核心Java平台。开发者可以创建让Java运行时当做认为是核心Java类的类和包,比如java.lang, java.util, java.net等。
3.strictfp
在Java中strictfp是可以用于类、方法或借口声明的修饰符,用于确保符合IEEE 754的精确浮点数算术。当对一个类或接口使用 strictfp 关键字时,该类中的所有代码,包括嵌套类型中的初始设定值和代码,都将严格地进行计算。严格约束意味着所有表达式的结果都必须是 IEEE 754 算法对操作数预期的结果,以单精度和双精度格式表示。
public class FPTest {
static strictfp double halfOfSquareFP(double n){
return n * 4.0 * 0.5;
}
static double halfOfSquareNFP(double n){
return n * 4.0 * 0.5;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d = 6.6e+307;
System.out.println(halfOfSquareFP(d));
System.out.println(halfOfSquareNFP(d));
}
}
4.动态类加载
Java中在运行时动态加载类的能力非常强大,动态类加载使得Java应用程序可以下载目标机器上没有的class文件。在一个机器上的对象类型可以无缝传输到其它机器。新的类型可以引入远程机器,可以在运行时扩展远程应用程序的行为。如下例子演示了远程应用程序接收类型实现某个接口:
public class MyRMIServer extends UnicastRemoteObject implements SomeInterface {
public MyRMIServer() throws RemoteException{ super();}
public String obtainName(IStockTicker ticker){
String stock_ticker = ticker.getTicker();
if(stock_ticker.equalsIgnoreCase("MSFT")) {
return "Microsoft Corporation";
} else if(stock_ticker.equalsIgnoreCase("SUNW")) {
return "Sun Microsystems";
} else {
return "Unknown Stock Ticker";
}
}
obtainName() 远程方法接收实现IStockTicker接口的类型,远程客户端可以调用这个方法然后传入实现IStockTicker的类型,例如NASDAQStock,如果MyRMIServer 所谓远程机器没有类的话,整个NASDAQStock 需要的类都会自动传输到远程机器。
5.包含字段的接口
在Java中,接口中可以声明常量,在实现的类中可以使用这个常量,这在C#中是没有的。这其实无关紧要,因为原先要这么这么用的主要原因是模拟枚举。
6.匿名内部类
匿名内部类是类的声明位于类创建实例内的类。匿名内部类一般用于在应用程序中只会有一个类的实例,最常用的就是在GUI类库中指定回调。如下是使用匿名内部类来实现状态设计模式的例子:
/* An instance of this class represents the current state of a ClientView GUI. */
public abstract class ClientState{
// This instance of the class is used to signify that the user is not logged in.
// The only thing a user can do in this state is login and exit.
public static ClientState NOT_LOGGED_IN = new ClientState() {
public void setMenuState(ClientView cv) {
cv.setMenuEnabledState(false); /* disable all menus */
cv.menuLogin.setEnabled(true);
cv.menuExit.setEnabled(true);
//can't type
cv.textArea.setEnabled(false);
}
public String toString(){
return "ClientState: NOT_LOGGED_IN";
}
};
// This instance of the class is used to signify that the user is logged in
// but has not yet created a document to work with. The user cannot type or save
// anything in this mode.
public static ClientState NO_OPEN_DOCUMENT = new ClientState() {
public void setMenuState(ClientView cv) {
cv.setMenuEnabledState(false); /* disable all menus */
cv.menuLogin.setEnabled(true);
cv.menuExit.setEnabled(true);
cv.menuOpenFile.setEnabled(true);
cv.menuNewFile.setEnabled(true);
//can't type
cv.textArea.setEnabled(false);
}
public String toString(){
return "ClientState: NO_OPEN_DOCUMENT";
}
};
// This instance of the class is used to signify that the user is editting a file.
// In this mode the user can use any functionality he/she sees fit.
public static ClientState EDITTING_DOCUMENT = new ClientState() {
public void setMenuState(ClientView cv) {
cv.setMenuEnabledState(true); /* enable all menus */
cv.textArea.setEnabled(true);
}
public String toString(){
return "ClientState:EDITTING_DOCUMENT";
}
};
// Default constructor private to stop people from directly creating instances
// of the class.
private ClientState() {;}
// This disables various elements of the ClientView's menu dependent on which
// ClientState object this is.
public abstract void setMenuState(ClientView cv);
}
如下是使用ClientState类的例子
bool loginUser(String username, String passwd) {
//check if already logged in
if(myGUI.state == ClientState.NOT_LOGGED_IN)
return true;
//enable parts of the GUI if the user authenticates
if(userAuthenticated(username, passwd)){
myGUI.state = ClientState.NO_OPEN_DOCUMENT;
myGUI.state.setMenuState(myView);
return true;
}
return false;
}
7.接口默认方法 (*Java 8)
Java中允许我们使用default关键字,为接口声明添加非抽象的方法实现。这个特性又被称为扩展方法。
interface Formula {
double calculate(int a);
default double sqrt(int a) {
return Math.sqrt(a);
}
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Formula formula = new Formula() {
@Override
public double calculate(int a) {
return sqrt(a * 100);
}
};
formula.calculate(100); // 100.0
formula.sqrt(16);
}
}
总结
本系列是对Java8和C#6.0的简单对比,参考和整理了许多网络和纸质资料,但因能力和精力都有限,所以难免有所遗落。但希望能对想要了解两门语言相同和不同之处的读者有所帮助。
参考资料
《深入理解C#》
《Java编程思想》
《CLR Via C#》
《C#入门经典》
《C#高级编程》
《.Net框架设计:配置、模式、工具》
《C#和Java比较》
Java5、Java6、Java7的新特性
Java 8简明教程
Java8的新特性以及与C#的比较
A COMPARISON OF MICROSOFT’S C# PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE TO SUN MICROSYSTEMS’ JAVA PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE
C#编程语言和JAVA编程语言的比较